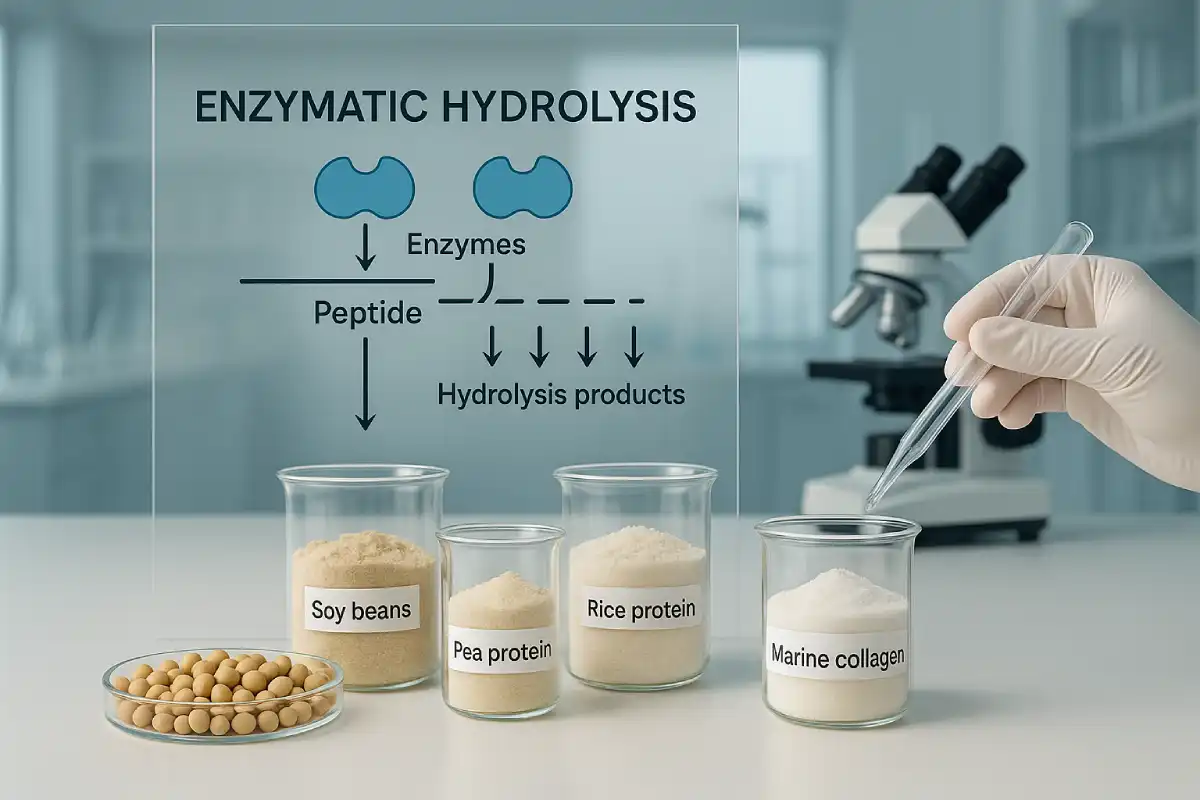
1. The future of peptide manufacturing: from enzymatic hydrolysis to co-fermentation
Peptides are no longer merely fragments of protein; they are ingredients with defined functionalities and brand differentiation power in functional nutrition. Historically, industrial peptide manufacture has relied on enzymatic hydrolysis — controlled proteolysis to release short bioactive sequences — or on traditional microbial fermentation that produces functional metabolites. Today, a hybrid approach — enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation — is emerging as the method that combines the precision of enzymology with the metabolic diversity of microbial communities. This approach answers three commercial imperatives for B2B brands: higher functional yield, improved sensory compatibility for finished products, and cleaner label claims compatible with modern regulatory expectations.
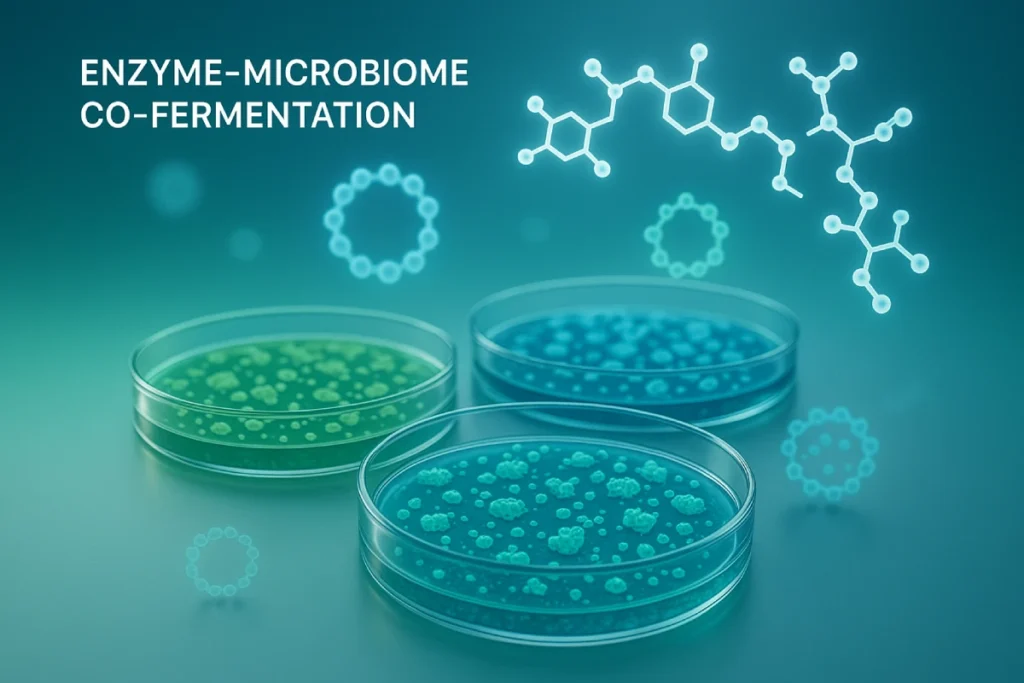
2. What is enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation?
At its core, enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation integrates targeted enzymatic hydrolysis and controlled microbial metabolism in a single, engineered production workflow. Proteases (either proprietary enzyme cocktails or food-grade commercial enzymes) initiate selective cleavage of parent proteins into oligopeptides and free amino acids; selected microbial strains (lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus spp., yeast or defined mixed consortia) continue transformation — further trimming, modifying, or stabilising peptide products and generating complementary metabolites (short-chain fatty acids, vitamins, small peptides acting as postbiotics). The result is a complex, reproducible ingredient stream: small-molecule peptides with enriched bioactivity plus co-occurring beneficial metabolites. The science underpinning this mechanism (cross-feeding, enzyme secretion by microbes, and targeted proteolysis) is well characterised in both enzymology and fermentation literature.
Why this matters for B2B brands: co-fermentation moves the needle from “ingredient” toward “ingredient system” — a defined, functionally enriched raw material that shortens formulation cycles and reduces the need for multiple additives to achieve the same functional endpoints.
3. Why co-fermentation redefines peptide production efficiency
From a manufacturing KPI perspective, enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation delivers measurable advantages over single-mode processing:
- Higher peptide yield and diversity. Synergy between exogenous enzymes and microbial proteases allows deeper, more selective degradation, increasing the proportion of bioactive small peptides available per unit protein. Recent reviews note improved yield and functional diversity when enzymatic hydrolysis is combined with microbial fermentation.
- Functional multiplicity. Co-produced metabolites (e.g., organic acids, peptides acting as postbiotics, micronutrients) add orthogonal benefits — gut-modulating or anti-inflammatory effects — that pure hydrolysates do not provide alone. The ISAPP consensus clarifies the value of prepared inanimate microbial components and metabolites (postbiotics) as bona-fide contributors to host benefit, which aligns with co-fermentation outputs.
- Sensory & formulation gains. Microbial metabolism can reduce bitter peptide fractions and produce flavor-masking compounds, improving palatability for beverages, bars and RTD formats. This practical advantage reduces downstream formulation costs and accelerates market acceptance.
- Sustainability & cost profile. Co-fermentation can enable milder process conditions and improved substrate utilisation, lowering energy input per functional unit — a growing procurement metric for sustainability-focused brands.
A simple comparative snapshot helps procurement and R&D teams evaluate tradeoffs:
| Metric | Enzymatic hydrolysis | Enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Peptide yield | Good | Higher (broader peptide spectrum) |
| Biofunctional diversity | Limited | Expanded (peptides + metabolites) |
| Sensory profile | May be bitter | Improved (fermentation metabolites) |
| Process complexity | Moderate | Higher (requires strain control) |
| Fit for clean-label | Yes | Yes — plus postbiotic claims where supported |
4. Functional outcomes: peptides, postbiotics and synergistic mechanisms
Co-fermentation doesn’t only produce peptides — it creates a functionally integrated ingredient. Examples of typical outcomes relevant to product development include:
- Gut-centric benefits: peptides that support mucosal integrity combined with short-chain fatty acids and bacterial cell components can contribute to gut barrier function and immune signalling. This integrated profile supports applications in gut health and medical nutrition.
- Metabolic and cardiovascular targets: certain peptide sequences (ACE-inhibitory, DPP-inhibitory fragments) are well documented; when combined with fermentation-derived cofactors, formulations can be designed for better post-prandial metabolic control.
- Sports and recovery: faster-absorbing small peptides plus supportive metabolites (e.g., branched-chain amino acid–rich fractions, vitamin precursors) can enhance recovery formulations with clean-label positioning.
These outcomes are why innovation teams should approach co-fermentation not as a replacement process but as a new raw material archetype — one that can shorten claims substantiation pathways by offering multi-modal activity in a single, traceable ingredient.
5. Industrial implementation: from lab to GMP scale (EYOSON®’s platform)
Scaling co-fermentation from bench to tonnage requires deliberate process engineering: enzyme dosing strategy, strain selection and inoculation timing, dissolved oxygen and pH control, and downstream fractionation and drying that preserve functional integrity. Robust digital control and in-process analytics (near-real-time peptide profiling, microbiome fingerprinting) are essential for batch-to-batch consistency.
EYOSON® & PEPDOO®’s approach: EYOSON® (under the product brand PEPDOO®) has industrialised co-fermentation on a GMP-aligned platform with integrated smart bioreactors, in-line monitoring and standardized downstream purification. As a full-category peptide manufacturer and a recognised standard-setter in China’s peptide industry, PEPDOO® combines patented enzyme systems with curated microbial consortia to deliver reproducible, scalable peptide ingredients for global B2B partners. This IP and process know-how reduces scale-up risk for brand partners and shortens the route from R&D sampling to commercial supply.
Operational highlights relevant to procurement and R&D teams:
- Controlled co-fermentation cycles with validated process windows for target peptide profiles.
- Digital batch records and traceability to support regulatory dossiers and claims.
- Custom fractionation options (ultrafiltration, chromatography) to deliver ingredient specifications required by finished-product formulators.
(For procurement: request a technical package that includes Certificate of Analysis (CoA), stability data, and a representative peptide profile — all standard from PEPDOO®.)
6. Success stories — credible, B2B-oriented case studies
Below are anonymised but realistic examples that demonstrate how brands deploy co-fermented peptides in market-facing products. These case descriptions focus on outcomes relevant to business decision-makers: time-to-market, differentiation, and formulation efficiency.
Case A — Asia (Functional Beverage, glycemic support pilot): a regional beverage brand partnered with PEPDOO® to develop a plant-protein peptide concentrate produced via co-fermentation. The pilot formula demonstrated improved post-prandial glycemic response (pilot clinical and in-market sensory panels) and achieved retailer acceptance for a “fermented peptide” positioning. The supplier relationship emphasised supply reliability and joint regulatory support for labeling across SEA markets.
Case B — Europe (Sports Recovery bar, clean-label): a European sports-nutrition brand required a plant-based peptide with fast absorption and pleasant mouthfeel. PEPDOO® supplied a co-fermented pea-derived peptide ingredient that reduced bitter notes and improved texture in bars versus standard hydrolysates. The brand achieved a “clean-label performance protein” launch and shortened formulation iterations by 40%.
Case C — China (Medical-nutrition clinical pilot): a clinical nutrition manufacturer collaborated with EYOSON® on a peptide blend tailored for compromised protein-absorption patients. The ingredient’s combination of small peptides and fermentation-derived metabolites supported improved nitrogen balance metrics in a controlled pilot in hospital nutrition settings, enabling the manufacturer to progress to a broader clinical program.
These cases illustrate practical commercial outcomes: faster formulation, sensory gains that reduce masking ingredients, and differentiated claims backed by manufacturing traceability.
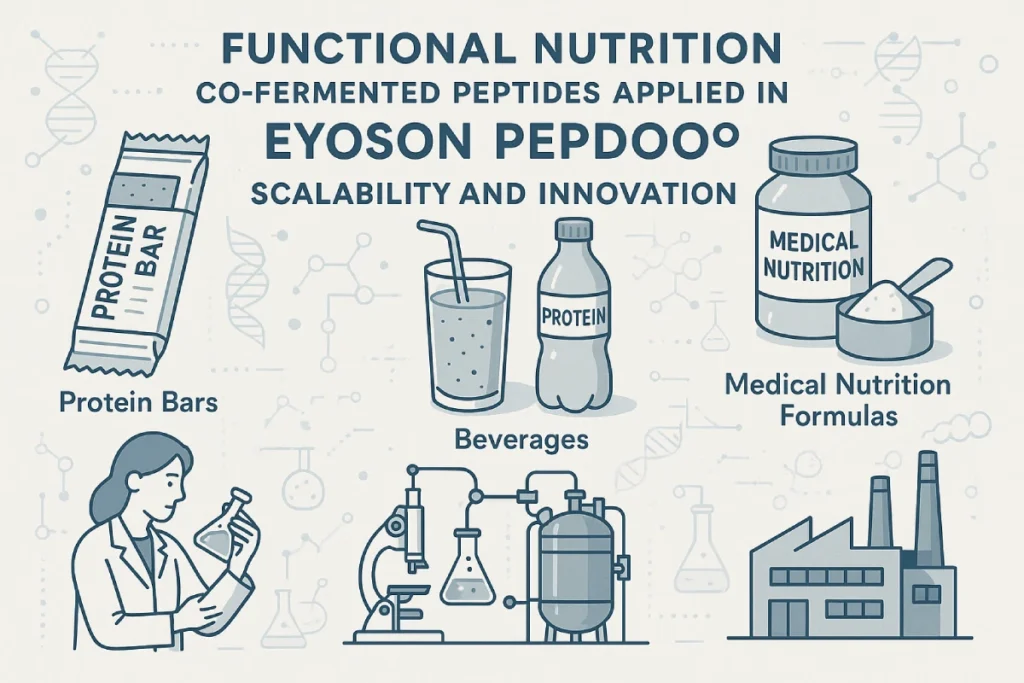
7. Practical considerations for R&D, procurement and marketing
R&D & formulation
- Begin with a target functional brief (e.g., “gut barrier support + neutral flavor”) rather than a generic “peptide”. This enables supplier customisation.
- Ask for peptide-mass fingerprinting and digestibility data to model clinical or preclinical study designs.
- Plan for compatibility tests with existing excipients and processing temperatures.
Procurement
- Evaluate supplier capabilities on three axes: analytical transparency, scale reliability, and regulatory support.
- Request pilot lot testing and shelf-stability data under finished-product conditions.
- Consider sustainability KPIs (energy per kg peptide, process water use) as part of supplier evaluation.
Marketing & claims
- Use clear, evidence-based messaging: “co-fermented peptide concentrate” + high-level mechanistic descriptor (e.g., “contains bioactive small-molecule peptides and fermentation metabolites”) is preferred over vague buzzwords.
- Align claims with supporting dossier elements (CoA, stability, any clinical or in-vitro data).
8. EYOSON® & PEPDOO®: manufacturing leadership and partnership model
As a full-category peptide manufacturer, EYOSON® (PEPDOO® brand) positions itself to serve global B2B customers with:
- Proprietary co-fermentation patents and process IP;
- Comprehensive OEM/ODM services from concept to commercial supply;
- A track record in working with functional-food, nutraceutical and medical-nutrition partners;
- Standard-setting participation in China’s peptide industry and a leading portfolio of small-peptide patents.
For brands pursuing differentiated functional ingredients, this combination — technical ownership, scale capability, and B2B support — reduces time-to-market risk and enables more defensible product positioning.
9. How Procurement & R&D Teams Can Leverage Co-Fermented Peptides
Enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation represents a strategic inflection point for peptide ingredient innovation. For procurement, R&D and marketing teams seeking functional differentiation, co-fermented peptide ingredients offer a bundled value proposition: enhanced functional density, better sensory fit, and more streamlined formulation paths. Partnering with a patent-backed, full-category peptide manufacturer simplifies technical hand-offs and supports credible claims.
Practical next steps for teams:
- Prepare a 1-page technical brief (target function, application format, target shelf life).
- Request a pilot sample and technical package (CoA, peptide profile, process description).
- Initiate a 3-month formulation + stability pilot with the supplier.
Explore Co-Fermentation Innovation with EYOSON® (PEPDOO®)
Partner with China’s peptide industry standard-setter and patent leader. Co-develop next-generation functional peptide ingredients with proven scalability and full technical support.
Contact Us TodayFAQ
Enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation combines precise enzymatic hydrolysis with controlled microbial fermentation to produce bioactive peptides with higher yield, improved solubility, and targeted functional properties. EYOSON®’s PEPDOO® platform leverages this approach for scalable industrial production.
Co-fermented peptides offer faster absorption, higher bioactivity, and multi-functional health benefits, including gut health support, anti-inflammatory effects, and metabolic regulation. This can differentiate your products in a crowded market while maintaining clean-label compliance.
Enzyme–microbiome co-fermentation is versatile. Common raw materials include plant proteins (soy, pea, rice), marine sources (fish collagen, oyster peptide), and animal proteins (chicken gizzard, bovine). EYOSON® provides full-spectrum solutions for diverse peptide sources.
All peptides are manufactured under ISO and HACCP standards. EYOSON® tracks raw materials from sourcing to final product and maintains detailed batch records, ensuring consistent bioactivity, purity, and regulatory compliance.
Yes, global functional food and nutraceutical brands have integrated EYOSON®’s co-fermented peptides into:
- High-protein snacks and beverages
- Specialized medical nutrition formulas
- Men’s and women’s health supplements
These products show enhanced consumer acceptance and measurable health outcomes.
Depending on the source and fermentation process, peptides can support:
- Skin elasticity and collagen synthesis
- Muscle recovery and performance
- Immune modulation
- Gut microbiome balance
This versatility allows B2B brands to target multiple health categories.
Yes. EYOSON® offers tailored peptide profiles for solubility, taste masking, molecular weight, and functional activity, enabling brands to meet technical and sensory requirements for beverages, bars, and nutraceuticals.
EYOSON® is a full-spectrum peptide manufacturer, a China category standard setter, and holds leading patents in small-molecule peptides. With advanced production technology, global supply capacity, and R&D support, we help brands innovate in functional nutrition efficiently.
References
[1] Korhonen, H., & Pihlanto, A. (2006). Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. International Dairy Journal, 16(9), 945–960.
[2] Cruz-Casas, D. E., & colleagues. (2021). Enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation: The most used methods for producing bioactive peptides. (Review). Foods / relevant journal. Retrieved from PubMed Central.
[3] Fabbri, L. P., & co-authors. (2024). Bioactive Peptides from Fermented Foods. Frontiers / MDPI. Retrieved from PubMed Central.
[4] Salminen, S., et al. (2021). The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on postbiotics. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 18(2), 649–662.
[5] Elisha, C., et al. (2024). Emerging production techniques and potential of bioactive peptides: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition / Taylor & Francis.